
Get a good code editor. You can use Notepad, but a more robust editor will make it easier to see the syntax of your VBScript code.WH.performance.mark('step1_rendered');
Get a good code editor.

Install Internet Explorer. Internet Explorer is the only browser that supports VBScript, as it is a proprietary Microsoft product. You will need Internet Explorer installed in order to see your VBScript in action.Since Internet Explorer is only supported on Windows, you will have the best results if you program on a Windows computer.
Install Internet Explorer.
Learn some basic VBScript practices. There are several important basics that it will be helpful to know before you dive too deep into coding.Use ' (apostrophe) to designate a comment. Any line that starts with an apostrophe is designated as a comment and is not processed by the script. Use comments often to help other developers, and yourself, figure out what the code is doing.Use _ (underscore) to extend the end of a line. The end of a line of code is typically designated by simply moving to the next line, but if the line becomes very long and needs to wrap to the next line, place a _ at the end of the unfinished line to indicate that the line continues on the next line.
Learn some basic VBScript practices.
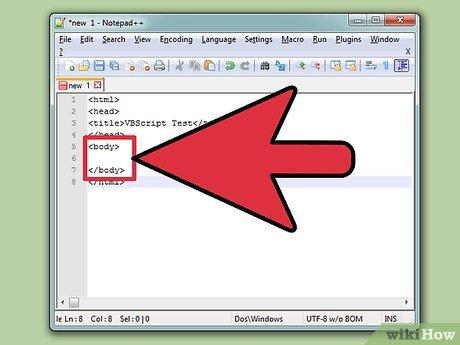
Create an HTML page. VBScript exists within HTML websites. In order to see your VBScript working, you will need to create an HTML file that you can open in Internet Explorer. If you have IE version 11 or higher, you need to switch on emulation for IE10 because IE11 does not support VBscript by default. If so, add this tag to the top of your vbscript code: <meta http-equiv='x-ua-compatible' content='IE=10'> Open your code editor and enter the following:[1] X Research source <html><head><title>VBScript Test</title></head><body></body></html>
Create an HTML page.
<meta http-equiv='x-ua-compatible' content='IE=10'>
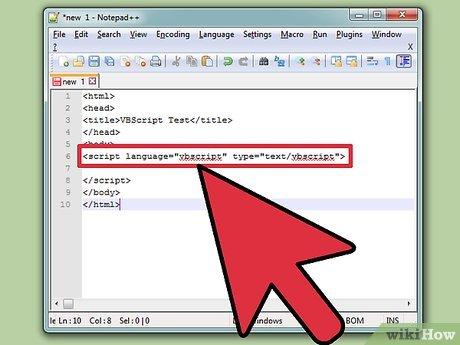
Add the VBScript tags. When creating a webpage with VBScript, you need to let the browser know that the script is coming up. Insert the tag into your HTML source:<html><head><title>VBScript Test</title></head><body><script language='vbscript' type='text/vbscript'></script></body></html>
Add the VBScript tags.
Use VBScript on an ASP server. If you are writing VBScript for an ASP server, you can indicate that the script is starting by using a special tag:<html><head><title>VBScript Test</title></head><body><%%></body></html>
Use VBScript on an ASP server.
Insert the Write command. This command is what displays content to the user. When using the write command, the designated text will be displayed in the browser.<html><head><title>VBScript Test</title></head><body><script language='vbscript' type='text/vbscript'>document.write()</script></body></html>
Insert the Write command.
Add the text that you want to be displayed. In the parentheses, add the text that you want to be displayed on the screen. Enclose the text with quotation marks to designate it as a string.<html><head><title>VBScript Test</title></head><body><script language='vbscript' type='text/vbscript'>document.write('Hello World!')</script></body></html>
Add the text that you want to be displayed.
Open the HTML file in your browser. Save your code as an .HTML file. Open the saved file using Internet Explorer. The page should display Hello World! in plain text.
Open the HTML file in your browser.
Declare your variables. Variables allow you to store data to be called upon and manipulated later. You need to declare variables using dim before assigning values to them. You can declare multiple variables at once. Variables must start with a letter, and can be up to 255 characters long. Below, we are creating the variable 'age':<html><head><title>VBScript Test</title></head><body><script language='vbscript' type='text/vbscript'>dim age</script></body></html>
Declare your variables.
Assign values to variable. Now that the variable has been declared, you can assign a value to it. Use the = sign to set the variable's value. You can use the Write command to display the variable on the screen to ensure everything is working<html><head><title>VBScript Test</title></head><body><script language='vbscript' type='text/vbscript'>dim ageage = 30document.write(age)</script></body></html>
Assign values to variable.
Manipulate your variables. You can use mathematical expressions to manipulate your variables. These expressions work much like basic algebra. All of your variables, including the answer, must be declared before using them.<html><head><title>VBScript Test</title></head><body><script language='vbscript' type='text/vbscript'>dim xdim ydim sumx = 10y = 5sum = x + ydocument.write(sum)'the page will display '15'</script></body></html>
Manipulate your variables.
Create an array. An array is essentially a table that can contain more than one value. The array is then treated as a single variable. Like variables, the array needs to be declared first. You must also indicate the number of values that the array can store (including 0 as the first number). You can then call on the data stored in the array later.<html><head><title>VBScript Test</title></head><body><script language='vbscript' type='text/vbscript'>Dim names(2)Dim mothernames(0) = 'John'names(1) = 'Jane'names(2) = 'Pat'mother = names(1)</script></body></html>
Create an array.
Create a two-dimensional array. You can create an array with multiple dimensions to store more data. When declaring the array, you will indicate the number of rows and columns contained in the array.<html><head><title>VBScript Test</title></head><body><script language='vbscript' type='text/vbscript'>Dim table(2,2)'This will create a 3x3 tabletable(0,0) = 'A' table(0,1) = 'B'table(0,2) = 'C'table(1,0) = 'D'table(1,1) = 'E'table(1,2) = 'F'table(2,0) = 'G'table(2,1) = 'H'table(2,2) = 'I'</script></body></html>
Create a two-dimensional array.
Understand the difference between 'sub' and 'function' procedures. There are two types of procedures in VBScript: sub and function. These two types of procedures allow your program to perform actions. Sub procedures can perform actions, but cannot return a value to the program. Function procedures can call other procedures as well as return values.
Understand the difference between 'sub' and 'function' procedures.
Make and call a sub procedure. You can use sub procedures to create tasks that your program can all on later. Use the Sub and End Sub statements to enclose the sub procedure. Use the Call statement to activate the sub procedure<html><head><title>VBScript Test</title></head><body><script language='vbscript' type='text/vbscript'>Sub mysubproc() document.write('This was written in a sub procedure')End SubCall mysubproc()'This will display the message written in the sub procedure</script></body></html>
Make and call a sub procedure.
Create a function procedure. A function procedure allows you to perform commands and return values to the program. Function procedures are where the meat of your programs functionality will occur. Use the Function and End Function statements to designate the contents of the function.<html><head><title>VBScript Test</title></head><body><script language='vbscript' type='text/vbscript'>Function multfunction(x,y)multfunction = x*yEnd Functiondocument.write(multfunction(4,5))'This will use your function and insert 4 and 5 into the x and y variables. 'The result will be printed on the screen.</script></body></html>
Create a function procedure.
Leave a Comment